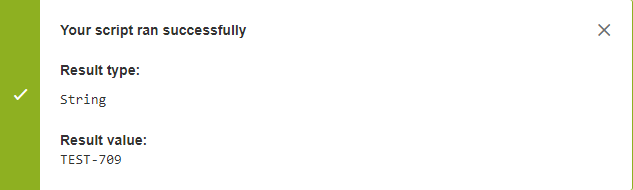JMCF provides a suite of custom fields for use in your JIRA instance, of which some calculated custom field types use a formula script written in the Groovy language to calculate/format the field value, such as:
- Calculate and display the author of the last comment on the issue
- Calculate and display the time spent in the current status
- Calculate and display the user has last modified a field value
Writing a Groovy
...
script in JMCF
A Groovy editor is provided in all the applicable custom field configuration screens to write your Groovy formulaescripts. You can either write them directly in the built-in editor, or use any IDE and then copy them to the editor. The built-in editor automatically indents your code, checks for syntax errors, colorizes keywords, comments, variables, and so on. JMCF includes a Groovy script tester tool that lets you test your formula script against any issue. This allows you to debug your formula script and make changes without having to actually save the configuration, refresh the issue or perform a re-index and look at the field value on the Issue view screen to see the outcome.
Writing a Groovy formulascript: In the custom field configuration screen of calculated custom fields that use Groovy formulascript, click on Edit Groovy expression or Edit Format expression, whichever is applicable. For example to write a formula script to access the key of an issue:
...
Testing the Groovy script: After writing the Groovy formulascript, click on Test Groovy Script. A modal dialog window opens, asking you to pick an issue to run the Groovy formula script against. Select an issue key. Click on Test. The result of the script is displayed.
Accessing Jira objects from your Groovy
...
script
An interface is a blueprint of a class. It has static constants and abstract methods. In JMCF you will be using the Groovy language and Jira APIs augmented by JMCF. The most common interface that you will be using in your formulae scripts is the Issue interface. This API provides the methods you can use on any Issue object. JMCF also exposes global variables and functions to access contextual information in your formulascript. For example, to access the issue being transitioned, you can use the global issue variable.
...
To log information in your formula script for debugging purposes, you can use the log global variable. You can use the WARN level to output information in the log as well as the tester result.
| Code Block |
|---|
log.warn("Reporter set by the formulascript is: " + newUser.name) //where newUser is a variable holding an ApplicationUser object |
JMCF has some more variables and global functions that are exposed to your Groovy formulaescripts.